What’s The Difference Between Prediabetes And Diabetes?
When it comes to metabolic disorders affecting blood sugar levels, prediabetes and diabetes are two terms that often cause confusion. Both conditions are linked to elevated blood sugar, but they represent distinct stages with varying implications for health and lifestyle. Understanding the difference between prediabetes and diabetes is crucial for early intervention, effective diabetes management, and overall well-being.
A Precursor to Diabetes
Prediabetes is a metabolic condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. This stage serves as a warning sign and an opportunity for individuals to make lifestyle changes that can prevent or delay the onset of full-blown diabetes.
Key Characteristics of Prediabetes
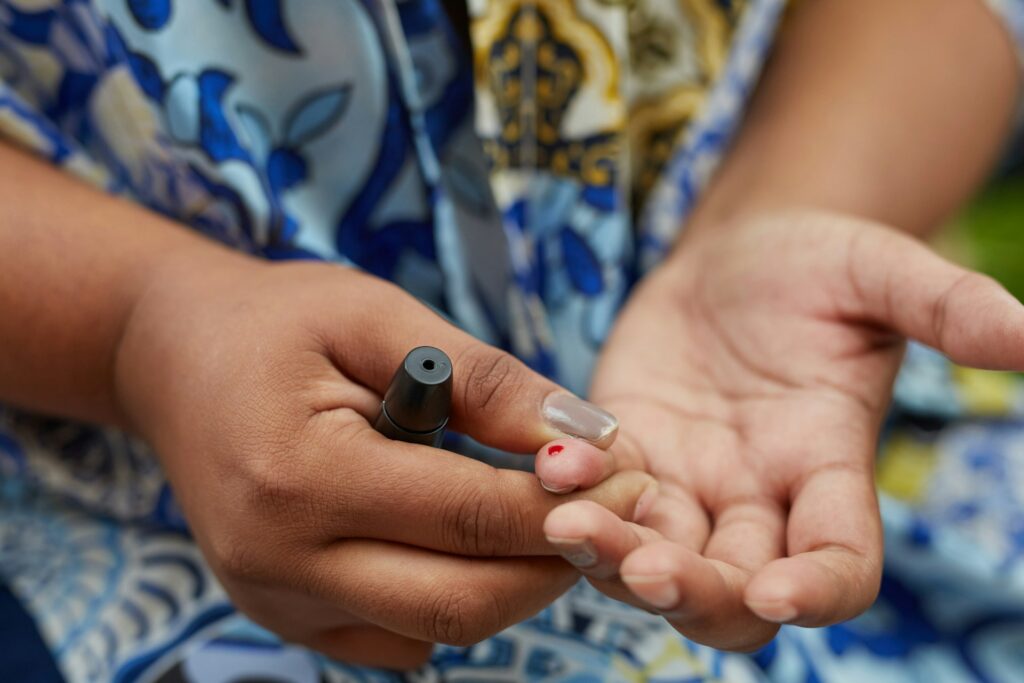
- Elevated Blood Sugar: Individuals with prediabetes have higher blood sugar levels than the normal range, as indicated by fasting blood sugar and hemoglobin A1c tests.
- Insulin Resistance: Prediabetes often involves a reduced sensitivity to insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar. This can lead to difficulty in controlling blood sugar levels.
- Risk Factors: Certain factors increase the risk of developing prediabetes, such as being overweight, leading a sedentary lifestyle, having a family history of diabetes, and age (being 45 or older).
- Symptomless Stage: Prediabetes may not exhibit noticeable symptoms, which underscores the importance of regular health check-ups.
- ● Reversible with Lifestyle Changes: The encouraging aspect of prediabetes is that it’s reversible. Through dietary adjustments, weight loss, and increased physical activity, one can lower blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of progression to diabetes.
Diabetes
Diabetes, on the other hand, is a chronic medical condition characterized by consistently high blood sugar levels. It occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or can’t effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes). Unlike prediabetes, diabetes requires ongoing medical management to prevent complications.
Key Characteristics of Diabetes
- Persistently High Blood Sugar: Diabetes is defined by elevated and sustained blood sugar levels, which can lead to a range of health complications if not managed properly.
- Types of Diabetes: There are two primary types of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition implicating the body’s immune system, destroying insulin-producing cells. Type 2 diabetes involves insulin resistance and is closely linked to lifestyle factors.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and slow wound healing.
- Long-Term Complications: Diabetes can lead to serious complications affecting the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Proper management through medication, insulin therapy, diet, and exercise is essential to prevent these complications.
- Lifestyle Management: While diabetes may not be completely curable, it can be effectively managed. A combination of medication, insulin (for Type 1 diabetes), blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management are integral to diabetes care.
Understanding the distinction between prediabetes and diabetes empowers individuals to take control of their health. If you’ve been diagnosed with prediabetes, consider it a wake-up call to make meaningful lifestyle changes. Engage in regular physical activity, adopt a balanced diet rich in fiber and whole foods, maintain a healthy weight, and monitor your blood sugar levels. These steps can significantly lower your risk of developing diabetes and its associated complications.
For those living with diabetes, adherence to a personalized management plan is paramount. Regular visits to healthcare providers, consistent blood sugar monitoring, and diligent medication or insulin use are fundamental. By actively managing diabetes, you can lead a fulfilling and healthy life.
Remember, your health journey is unique, so consult healthcare professionals for personalized guidance. We will also support you on this journey. To learn more about prediabetes, diabetes, and holistic health management, explore our comprehensive services. Start today for a healthier tomorrow.
The difference between prediabetes and diabetes lies in their stages, characteristics, and management approaches. Prediabetes acts as an early warning sign, offering an opportunity for lifestyle adjustments to prevent diabetes. Diabetes, a chronic condition, requires ongoing management to prevent complications. By understanding these differences and taking proactive steps, you can pave the way for a healthier and more vibrant life.